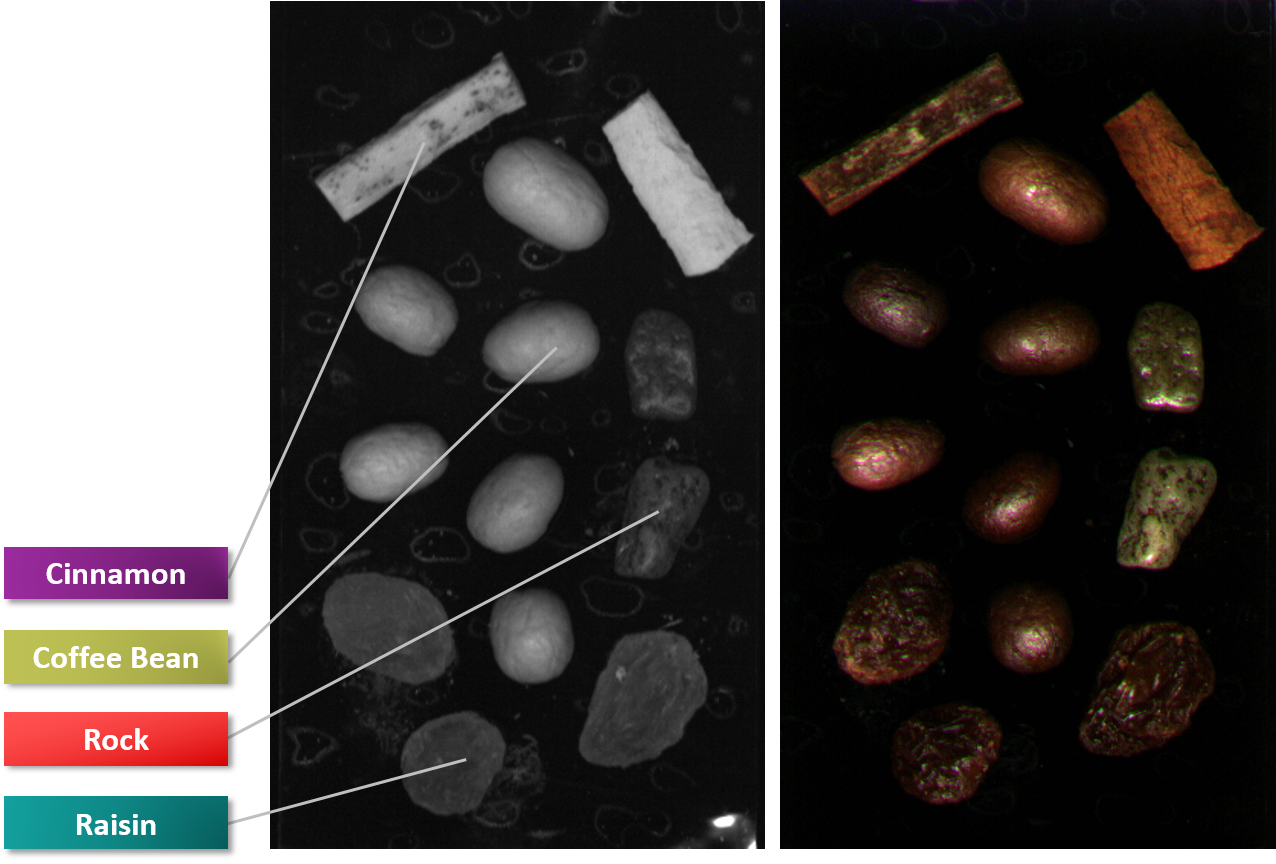
What are Line Scan Cameras?
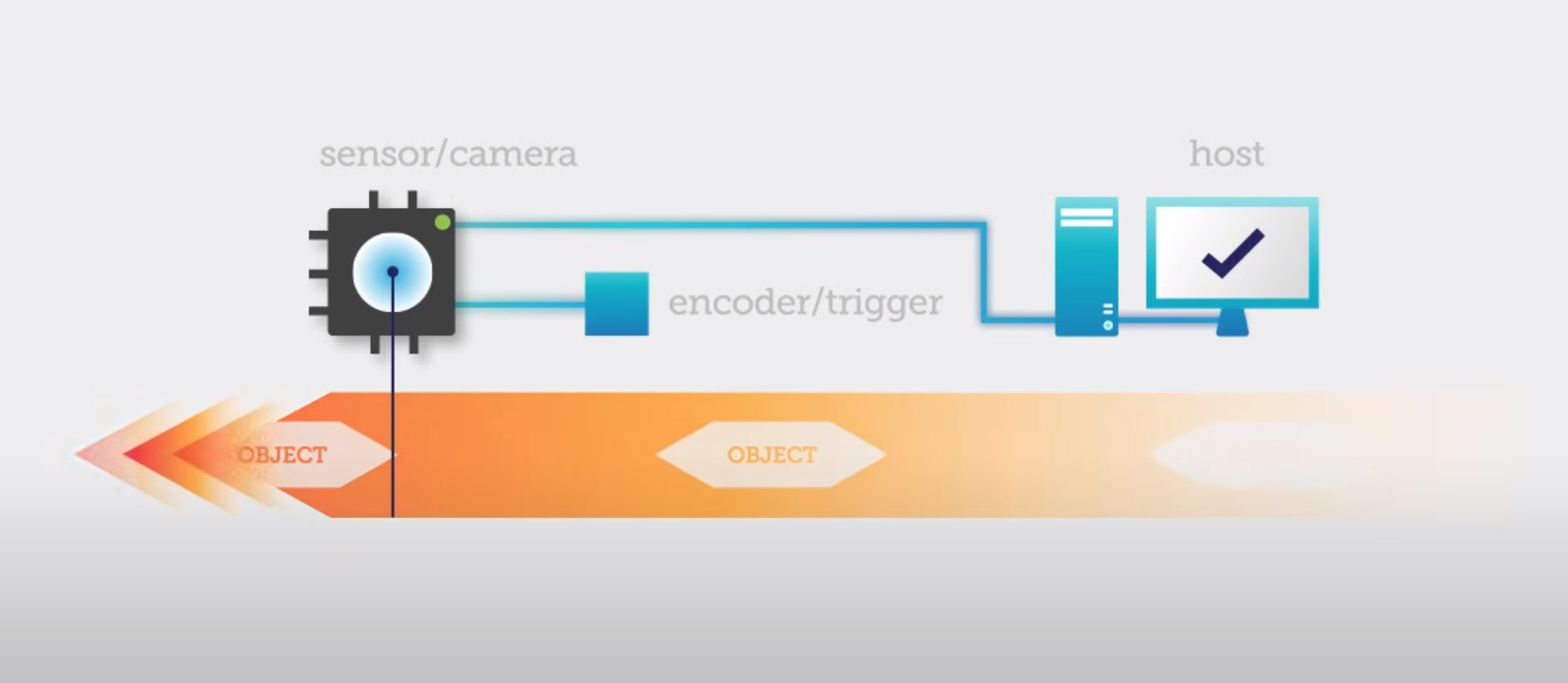
A household document scanner is the most common example of line scan imaging. Line scan imaging uses a single line of sensor pixels (effectively one-dimensional) to build up a two-dimensional image. The relative motion between the image sensor and the object being scanned provides the second dimension. With speed synchronization, images are joined line-by-line to give a 2D image.
Generally to view objects moving at speed, a Single line scan camera works better than Two Area Scan Cameras in terms of high resolution and without the extra work of overlapping and redundant data.
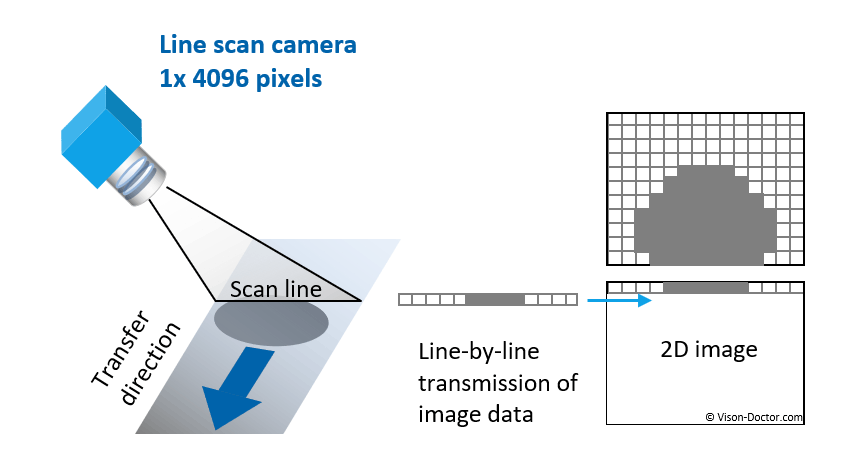
Representation of image formation with line scan cameras
With the object moving in one direction, the camera captures line-by-line. An on-board or external processor then joins the lines together to form the image.
Advantages of Line Scan Cameras
Save Space and Cost
Line Scan Camera Systems are generally more compact, enabling them to fit in space restricted environments. They provide a lower cost per pixel due to high resolution in scanning and an infinite resolution for moving objects.
High Resolution. No Blur. No Distortion.
A bright light is required to illuminate the line being scanned. Each line capture is extremely fast and free from smear due to object motion. The images also have higher dynamic range as compared to other image capturing methods.
Easy Lighting. Fast Processing.
Since the scanned line only needs to be illuminated, this simplifies the lighting setup and reduces effects of reflection. Fast processing is achieved by transmitting and scanning a line in parallel. Reduced data redundancy and overlap also makes processing faster.
Line Scan Camera Applications
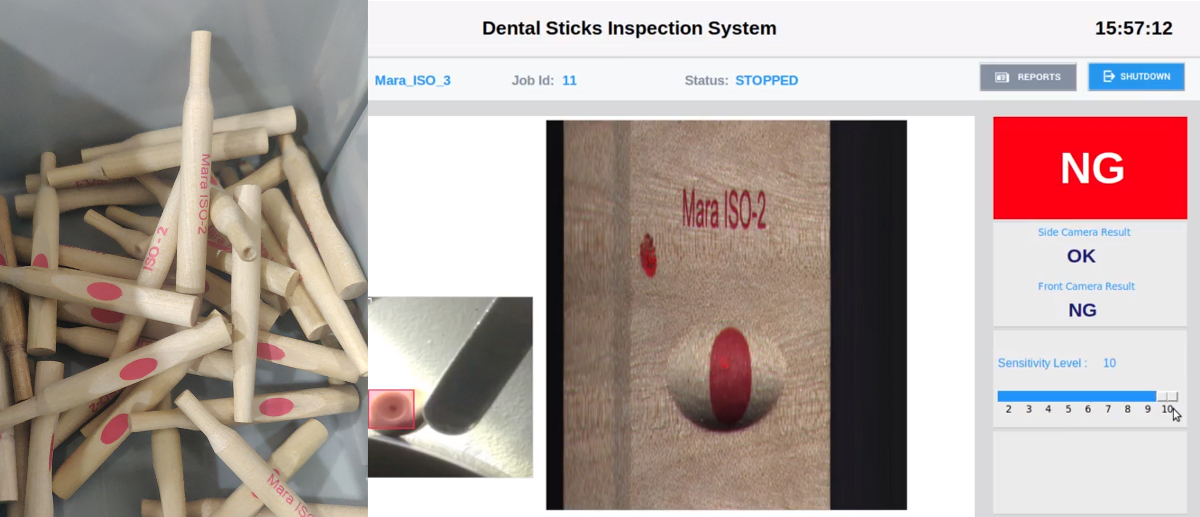
Sticks Inspection

Weaving Defects
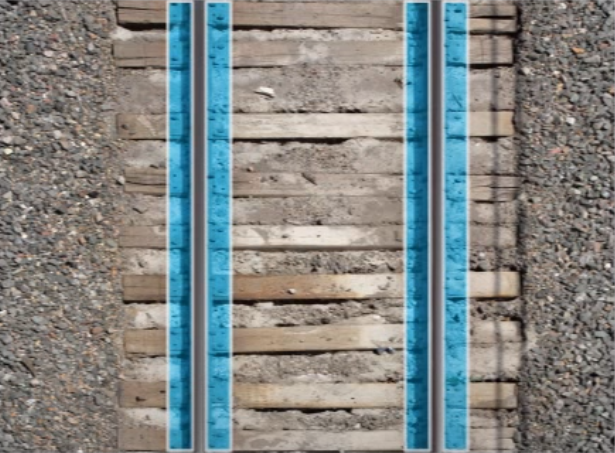

Railway Inspection
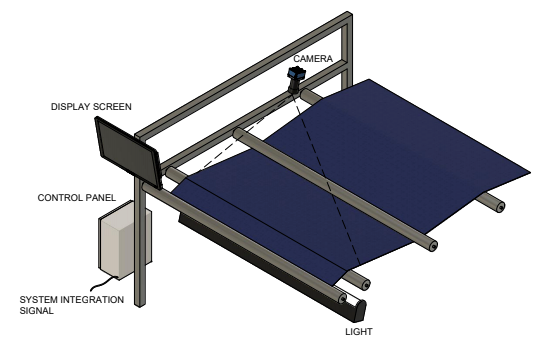
Textile Inspection
Object Inspection

Print Inspection
Wafer Inspection